General Information
The Yale Blood Disease Reference laboratory Program (BDRLP) has been established as a national reference laboratory under Yale's CLIA certified Molecular Diagnostic Pathology Laboratory. The function of the BDRLP is to provide a resource to physicians and their patients for the diagnosis of complex hereditary intrinsic red cell disorders, particularly those involving defects in the cell's plasma membrane.
The plasma membrane provides structural support for the anucleate erythrocyte, accounting for its antigenic, transport, and mechanical characteristics. Inherited red cell disorders with altered membrane and cell function can be broadly divided into two categories: 1) altered function due to mutations in various membrane, skeletal, or metabolic proteins, such conditions include hereditary spherocytosis (HS), hereditary ellipotocytosis (HE), hereditary ovalocytosis, and hereditary stomatocytosis; and 2) altered function due to secondary effects on the membrane resulting from mutations in globin genes; these conditions include sickle cell disease, Hb SC disease, Hb CC disease, unstable hemoglobins, and thalassemias. As a result of natural selection driven by severe forms of malaria and other diseases affecting the red cell, 1 in 6 individuals in the world; more than 1 billion people are affected by red cell abnormalities. Such diseases are thus the most common of all inherited disorders.
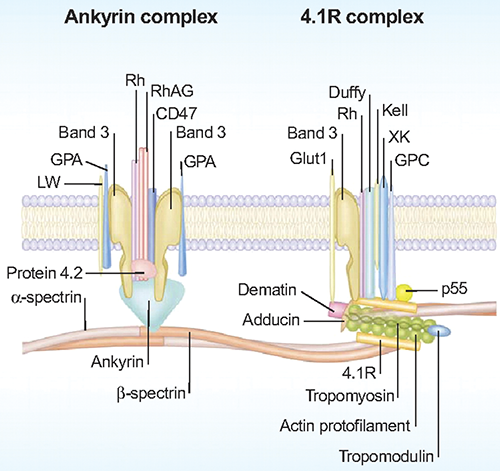
Schematic representation of red cell membrane
Specimen Preparation
Specimen Preparation: Whole blood samples of at least 5 ml in EDTA anticoagulant (Purple Tube) should be submitted at room temperature. The appropriate billing mechanism should be established before the specimen is admitted for testing. A consent form signed by the patient or the guardian should be obtained and filed by the submitting physician.
Mailing address for sample submission:
Blood Disease Reference Laboratory
Department of Pathology
310 Cedar Street, CB 541a
New Haven, CT 06520
Tel. 203-737-1349 Fax 203-785-3896
Yale Blood Cell Disease Reference Laboratory Programs: Rapid Mutation Scanning by Next Generation Sequencing
Pei Hui, MD, PhD, Vincent Shultz, PhD, Michael Krauthammer, PhD, Matthew Holford, BA, Suping Chen, MS, Teresa Silva, MS, Patrick Gallagher, MD and Jon Morrow, MD, PhD