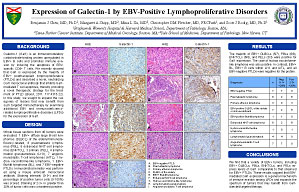
Expression of Galectin-1 by EBV-Positive Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Benjamin J Chen, MD, PhD1, Margaret A Shipp, MD2, Mina L Xu, MD3, Christopher DM Fletcher, MD, FRCPath1, and Scott J Rodig, MD, PhD1
1Brigham & Women's Hospital & Harvard Medical School, Department of Pathology, Boston, MA; 2Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Department of Medical Oncology, Boston, MA; 3Yale School of Medicine, Department of Pathology, New Haven, CT
BACKGROUND
Galectin-1 (Gal1) is an immunomodulatory carbohydrate-binding protein upregulated in EBV+ B cells and promotes immune evasion by inducing the apoptosis of EBV-specific CD8+ T cells. We recently showed that Gal1 is expressed by the majority of EBV+ posttransplant lymphoproliferative (PTLDs) and described a novel, neutralizing Gal1 monoclonal antibody that inhibits Gal1-mediated T cell apoptosis, thereby providing a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of PTLD (Blood, 2011. 117:4315-22). In this study, we sought to expand the categories of lesions that may benefit from such targeted immunotherapy by examining additional EBV and immunodeficiency-related lymphoproliferative disorders (LPDs) for the expression of Gal1.
©2012 Yale Department of Pathology. All rights reserved.
Any redistribution or reproduction of part or all of the contents in any form is prohibited. You may not, except with express written permission of the author or the Department of Pathology, distribute or commercially exploit the content, nor may you transmit it or store it in any other website or other form of electronic retrieval system, including use for educational purposes.